Table of Contents
SaaS and cloud computing are two related technologies that business leaders consider when evaluating technology options to build software to run their businesses.
Despite not precisely being a chicken-and-the-egg paradox, Software as a Service (SaaS) wouldn’t be possible without the cloud. Even yet, SaaS and cloud computing are two phrases that people frequently conflate. Overall, the term “Cloud Computing” is an umbrella term that refers to on-demand access to a variety of computing resources consisting of IaaS, PaaS and SaaS which benefits businesses in terms of flexibility and cost saving.
This post will explain how SaaS and cloud computing relate to one another, and how they benefit businesses moving to the cloud.

The Ultimate Checklist for Building An Incredible SaaS Product
Get your free copy
SaaS is a subset of cloud computing.
Through SaaS, the software is delivered and made accessible over the Internet. Using SaaS, you can subscribe to already developed software, through a monthly or annual subscription, without having to maintain it.
Let’s get started!
SaaS Vs Cloud Computing
The delivery of scalable and elastic IT-enabled capabilities as a service through the internet is known as “cloud computing.”
Software that is owned, supplied, and managed remotely by one or more providers is known as software as a service (SaaS). In a one-to-many approach, the provider delivers software that is consumed at any time by all of the contracted clients on a pay-per-use basis or as a subscription depending on use metrics. – Gartner Glossary
SaaS and cloud computing both provide similar advantages to users and are offered via the Internet. They don’t exist on the user’s computer or a company server, therefore they don’t need tedious installations or ongoing maintenance. On the “server side,” all software updates, installations, ongoing maintenance, etc. issues are handled. SaaS and cloud computing are both available by subscription and are instantly accessible from any location where a user has an Internet connection.
What is SaaS Development?
Every organization needs a specific set of software products to function. A multinational team that works remotely can benefit from regular meetings conducted via email or an app. One can benefit from SaaS development services because the traditional approach of hosting one’s infrastructure, software, and app can be costly and time-consuming.
SaaS enables users to access cloud-based tools and applications for everyday use. Managing projects and tasks, the sales pipeline, customer assistance, collaboration, knowledge management, and many more corporate applications all use this common delivery paradigm.
SaaS vendors typically charge monthly or yearly subscription fees. Whereas, in traditional software services, the organizations pay for a one-time license fee along with additional charges for support & maintenance.
Some SaaS providers offer apps that follow the freemium business model. This paradigm helps users in understanding the complexities and assessing whether the application answers their concerns.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the on-demand use of computer resources hosted in a distant data center and controlled by a cloud service provider (CSP), such as applications, servers (both physical and virtual), data storage, development tools, networking capabilities, and more. These resources are made available by the CSP for a monthly subscription fee or are billed based on usage.
It can be time-consuming and expensive to understand the different kinds of cloud computing resources. To have the cloud computing architecture, businesses need to purchase physical servers and other hardware through procurement procedures that can take months and years. Physical space is needed for the acquired systems, often a specific room with enough power and cooling. Enterprises require qualified employees to manage the systems after they have been configured and deployed.
When demand increases or a company grows, it is challenging to scale this lengthy process. Businesses may purchase more computing resources than necessary, resulting in low utilization rates.
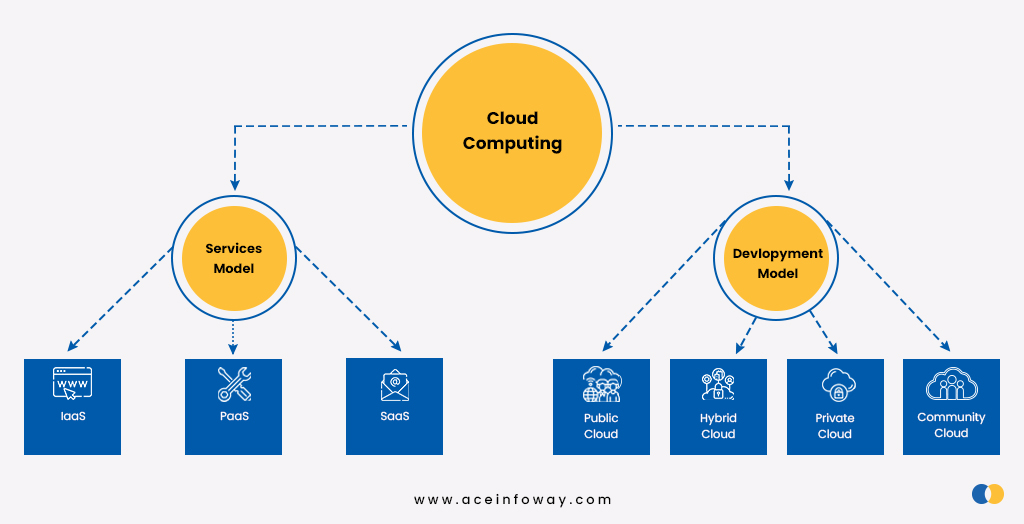
These problems are addressed by cloud computing. Also, there are various types of service models and deployment models in cloud computing that are listed below in detail:
Various Service Models in Cloud Computing
1⃣ IaaS
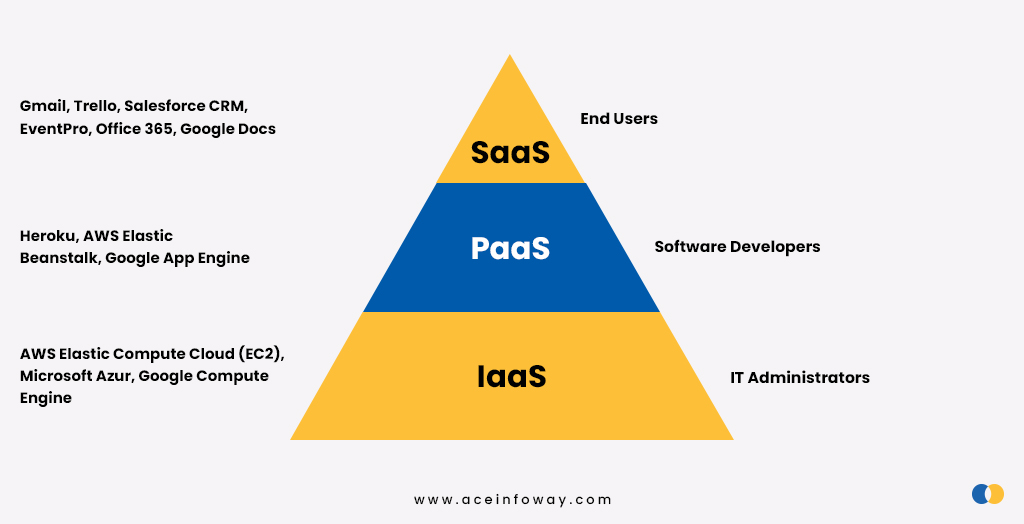
IaaS includes access to data center resources, virtual servers, cloud storage, and cloud security (managed by the IaaS provider).
The term “infrastructure” in the context of computing refers to the computers and servers that run code and store data as well as the cables and other devices that connect them. For instance, infrastructure includes routers, servers, and hard drives. Before cloud computing became a possibility, the majority of companies hosted their infrastructure and ran all of their software on-premise.
In an IaaS model, a company—of any size—uses a cloud provider to obtain services like computing, storage, and databases. By hosting hardware and software in the cloud, the cloud provider makes such services available. The cost structure changes to a pay-as-you-go model because the business no longer needs to acquire and maintain its server & software or space to host that server & software. Less is paid for when a business requires fewer services. Additionally, as the company grows, it can quickly provision more computing resources and other software services.
IaaS service provider: DigitalOcean, Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Computing Engine (GCE), Linode, etc.
2⃣ PaaS
PaaS service provider: Platform-as-a-Service, also known as PaaS, is a cloud computing model that offers customers a full cloud platform—including hardware, software, and infrastructure—for creating, deploying, and managing applications without the expense and complexity.
Like IaaS, PaaS also comprises infrastructure- servers, storage, and networking but also comprises middleware, development tools, business intelligence (BI) services, database management systems, and other things. PaaS is made to handle the entire lifetime of a web application, including development, testing, deployment, management, and updating.
Everything is hosted at the PaaS provider’s data center, including servers, networks, storage, operating system software, databases, and development tools. Customers often have two options: they can choose ‘pay-as-you-go’ pricing to pay only for the resources they use, or they can pay a fixed charge to supply a certain amount of resources for a certain number of users. With either choice, PaaS users may create, test, deploy, run, update, and grow applications more quickly and affordably than they could if they had to develop and maintain their on-premises platform.
PaaS service provider: AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Oracle Cloud Platform, Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure, IBM Cloud Platform, etc.
3⃣ SaaS
SaaS (software as a service) enables users to access and use cloud-based applications over the Internet. Email, calendaring, and office tools (such as Microsoft Office 365) are common examples.
Software as a Service, or SaaS, is a cloud-based service provider where you access an application through an internet browser rather than downloading software on your desktop, PC, or company network to operate and update. The software app could be anything from office software to unified communications, among a vast range of other readily available business apps.
You can avoid complicated software and hardware maintenance by just accessing software over the Internet rather than installing and maintaining it.
SaaS applications are also referred to as hosted software, web-based software, and on-demand software. Whatever name they go by, SaaS applications run on the servers of a SaaS provider. Security, reliability, and performance of application access are all managed by the provider.
SaaS gives businesses a number of benefits, particularly in terms of flexibility and cost-savings. Employees can concentrate on other priorities when SaaS companies handle the tiresome activities like installing, managing, and updating software.
Various Deployment Model in Cloud Computing
1⃣ Public Cloud
Public cloud deployments are often kept on open servers that can be accessed over the internet via a VPN. The service owner often owns the hardware and software used in these facilities. For businesses who do not want to purchase their own application server, storage, CPU, OS, database, etc., this saves them a significant sum of money.
This deployment also saves money by not requiring additional people to service and maintain the components. You can also quickly add new services and expand your business without needing to hire more staff.
Public clouds are mostly used for application development, file sharing, email services, and testing.
2⃣ Private Cloud
Despite some technical similarities, the ownership of these services is the key distinction between publicly accessible cloud platforms and privately owned ones. You won’t be able to access the platform if you don’t have permission to use it.
A business has the option to have its own private cloud platform or run it on-premise. The fact that a private cloud is maintained by the company’s team is another factor in its flawless operation. This guarantees that the systems are created and operated in accordance with the requirements of the business.
Medical companies, banks, and organizations subject to state-mandated data all use private cloud deployments.
3⃣ Community Cloud
The only significant difference between community and private cloud is its user base. A community type involves numerous organizations with similar backgrounds sharing the infrastructure and associated resources, in contrast to a private type where it is considered that only one company owns the server.
Community cloud is the best option for joint business organizations, partnerships, research organizations, and tenders. Before selecting community cloud organizations or users need to know and analyze the business demand first.
4⃣ Hybrid Cloud
Another type of cloud computing is hybrid cloud, which combines two or more cloud servers—private, public, or community—into a single architecture while maintaining their individualities. While non-critical tasks like development and test workloads can be completed using a public cloud, sensitive critical tasks like managing organizational data are best completed utilizing a private cloud. A hybrid cloud hosting environment allows for the benefits of both deployment models as well as a community deployment methodology.
The hybrid cloud deployment strategy not only maintains and preserves strategically vital assets, it also does so in the most economical and resource-efficient manner for each unique situation. Additionally, this method makes it easier to port data and applications.

The Ultimate Checklist for Building An Incredible SaaS Product
Get your free copy
List of Popular Cloud Service Provider
We have listed few cloud service provider that have made the most impacts in 2022:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Azure
- Google Cloud Platform
- Oracle Cloud
- IBM Cloud
- Alibaba Cloud
- Tencent Cloud
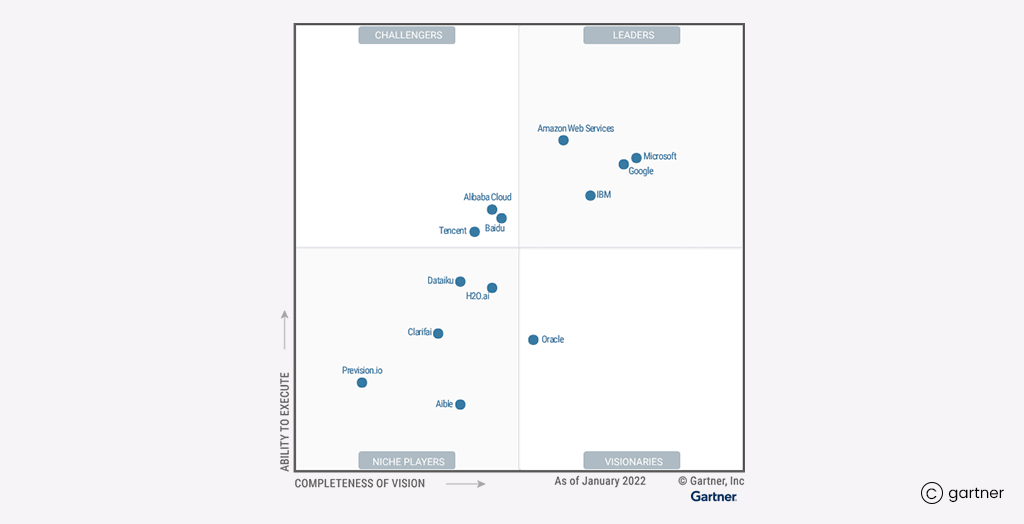
Magic Quadrant for Cloud AI Developer Services- Gartner
Saas and Cloud Computing- The Relation Between the Two
SaaS is a subset of cloud computing. It’s crucial to remember that not all SaaS solutions are cloud-based. Applications or SaaS products can be created locally and then deployed to a cloud-based server. A web browser is used to access and use the actual product. Cloud software has three subcategories: IaaS, PaaS and SaaS
Products that are SaaS-based have two essential characteristics. The software is immediately served to you, hosted, pre-configured, and ready to use; this is the first characteristic. This drastically decreases entry-level barriers to the market because there is nothing to install, buy, or worry about the hardware. You do not own the software, which is the second characteristic. With SaaS, you are paying for a service rather than buying the software altogether. This usually applies to a subscription model, where you pay for the service on a monthly or annual basis.
Faster installation times and the hosting company would take care of any necessary upgrades in the future are two benefits of SaaS applications. Gmail, a mail service offered by Google, is a great example.
On the other hand, cloud computing provides solutions that can be utilized to create a unified approach to cloud-based data storage, as well as services similar to SaaS apps. It can include PaaS products that developers can use to design, test, and deploy software as well as IaaS solutions or an IaaS model that permits the use of servers, data centers, and security resources to manage essential business activities. These opportunities come together as one when a whole cloud computing solution is implemented rather than existing as separate elements.
| SaaS | Cloud |
|---|---|
| Today, SaaS is prevalent in every industry sector. Here are some of the most common apps: | There is a list of applications that are developed in all business segments and categories; here are some of the most common ones: |
| CRM | Online file storage |
| Business Intelligence | Web app for antivirus |
| Collaboration/communication/social | Spreadsheets |
| Customer service support | Presentation software |
| Budgeting/ reporting/ planning | Digital video software |
| Finance accounting | Photo editing software |
| ERP/manufacturing/supply chain | Word processing application |
Future of Cloud-Based Products
Gartner estimates that global spending on public cloud products would likely exceed $600 billion in 2023, expanding at a rate of 20.4% per year.
According to Gartner, end-user spending on Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) would increase by 30.6% in the coming year. The growth forecast is 26.1% for Platform as a Service (PaaS).
Organizations spend an estimated $2.6 billion annually on cloud migration projects due to the growing trend of hybrid work.
Given end-user demand for cloud native capabilities, PaaS investment will probably rise to $109.6 billion. According to Gartner, by 2025, public cloud service investment will surpass traditional IT spending.
The “Cloud Shift” survey by Gartner exclusively examines IT market categories that can move to the cloud. By 2024, cloud computing will replace traditional solutions for more than 45% of IT spending on system infrastructure, infrastructure software, application software, and business process outsourcing.
Conclusion
We hope that this article has helped you understand what SaaS and Cloud Computing is. SaaS is generally best adapted for smaller businesses that require low-cost solutions for their needs. On the other hand, cloud computing makes more sense for larger businesses that have more resources, need or desire more control over sensitive data, and can easily afford the cost of this type of infrastructure.