Table of Contents
In 2024, mobile app revenue is projected to hit $171 billion annually. As businesses and innovators scramble to capture their share of this booming market, it becomes paramount to understand the intricacies of mobile app development. But first, a profound understanding of the landscape is the bedrock upon which innovative apps are built. And to develop next-gen apps, it’s essential to grasp some of the most emerging trends in the industry today.
Businesses today are revolutionizing user experiences by integrating AI and ML for hyper-personalization, leveraging AR technology to create immersive interfaces, embracing the transformative potential of 5G networks, and adopting predictive analytics to enhance UI/UX, fostering increased engagement and user retention. These emerging trends in mobile app development signify a crucial step towards elevating user satisfaction and interaction in the digital landscape.

Mobile App Accessibility Guidelines
Get your free copy
Ready to create your app? Learn these 5 steps that bring your ideas to life.
What are the 5 Stages of Mobile App Development?
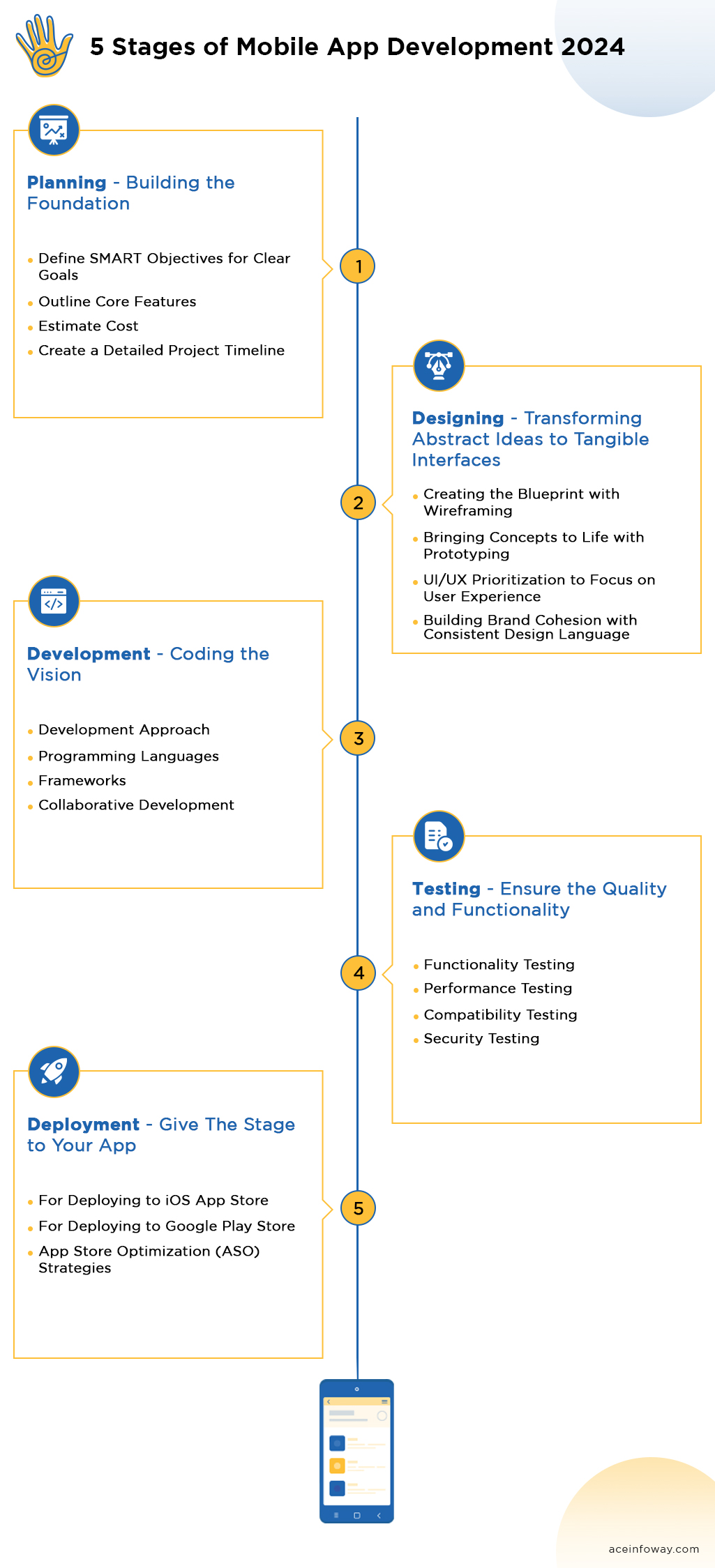
Step 1: Planning – Building the Foundation

1) Define SMART Objectives for Clear Goals
- Specific Objectives: Clearly state what the app intends to achieve. For instance, if the goal is to increase user engagement, specify the methods and metrics to measure engagement.
- Measurable Metrics: Establish quantifiable parameters such as user engagement rates, app downloads, or revenue. These metrics provide tangible data to evaluate the app’s performance.
- Achievable Targets: Set realistic goals that are attainable within the available resources and technological constraints. Unrealistic objectives can lead to frustration and project delays.
- Relevance: Ensure the goals align with the app’s purpose, user needs, and market demands. Relevance ensures that efforts are channeled toward meaningful outcomes.
- Time-Bound Deadlines: Implement a strict timeline by breaking down the goals into manageable milestones within designated timeframes. Time-bound objectives provide a sense of urgency and facilitate progress tracking.
2) Outline Core Features
- User Research: Conduct in-depth research to understand user preferences, pain points, and expectations. User research helps in identifying features that directly cater to user needs.
- Market Demands: Align features with current market trends and demands. Market analysis tools aid in identifying features that are popular among users, ensuring the app remains relevant and competitive.
- Prioritization: Rank features based on their importance and relevance to the core app functionality. Prioritizing features ensures that the most essential elements are developed first, optimizing the app’s user experience.
- Scalability: Consider how features can accommodate future enhancements without requiring major changes to the app’s architecture. Scalable features allow for the app’s evolution in response to changing user demands.
3) Estimate Cost
- Development Costs: Evaluate expenses related to coding, programming languages, third-party integrations, and app functionalities. This assessment helps in budgeting the development phase effectively.
- Design Expenses: Include costs associated with UI/UX design elements, graphic assets, and branding materials. A visually appealing design enhances user engagement and satisfaction.
- Infrastructure Costs: Account for server space, databases, APIs, and cloud services. Infrastructure costs ensure the app’s seamless functioning and data management.
- Contingency Budget: Allocate a portion of the budget for unforeseen expenses and emergencies. A contingency budget provides financial preparedness for unexpected challenges, preventing budget overruns.
4) Create a Detailed Project Timeline
- Milestone Setting: Divide the project into specific milestones, each representing a significant phase of development. Milestones provide clear markers of progress.
- Deadline Assignments: Assign realistic deadlines for each milestone. Deadlines create a sense of urgency, ensuring tasks are completed in a timely manner.
- Regular Progress Tracking: Implement regular progress checks against the established timeline. Regular tracking identifies potential delays and allows for corrective actions, maintaining project momentum.
- Flexibility: While adhering to deadlines is essential, maintain flexibility to adapt the timeline based on unexpected challenges or opportunities. Flexibility ensures adaptability to evolving project requirements.
Step 2: Designing – Transforming Abstract Ideas to Tangible Interfaces

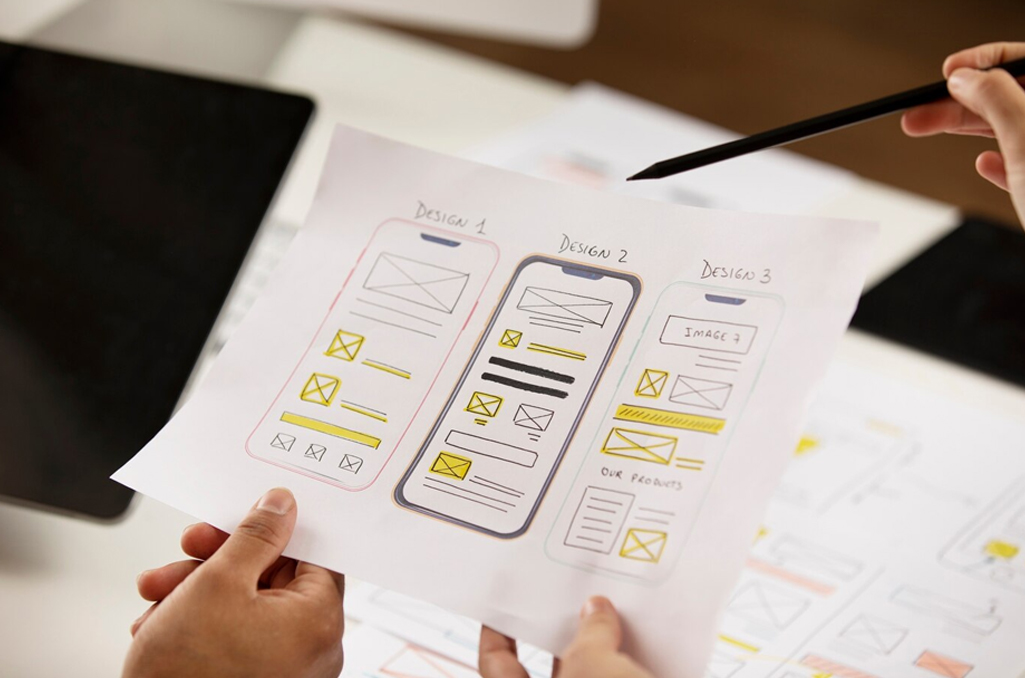
1) Creating the Blueprint with Wireframing
- Skeletal Structures: Wireframes are like the architectural blueprints of the app. They are basic, low-fidelity layouts representing the structure of the user interface. Wireframes outline where elements like buttons, menus, and images will be placed, focusing purely on layout and functionality.
- Focus on Functionality: Wireframes prioritize the arrangement of elements to ensure logical flow and ease of use. They act as a visual guide for developers, ensuring the app’s fundamental structure is sound before moving to more detailed design stages.
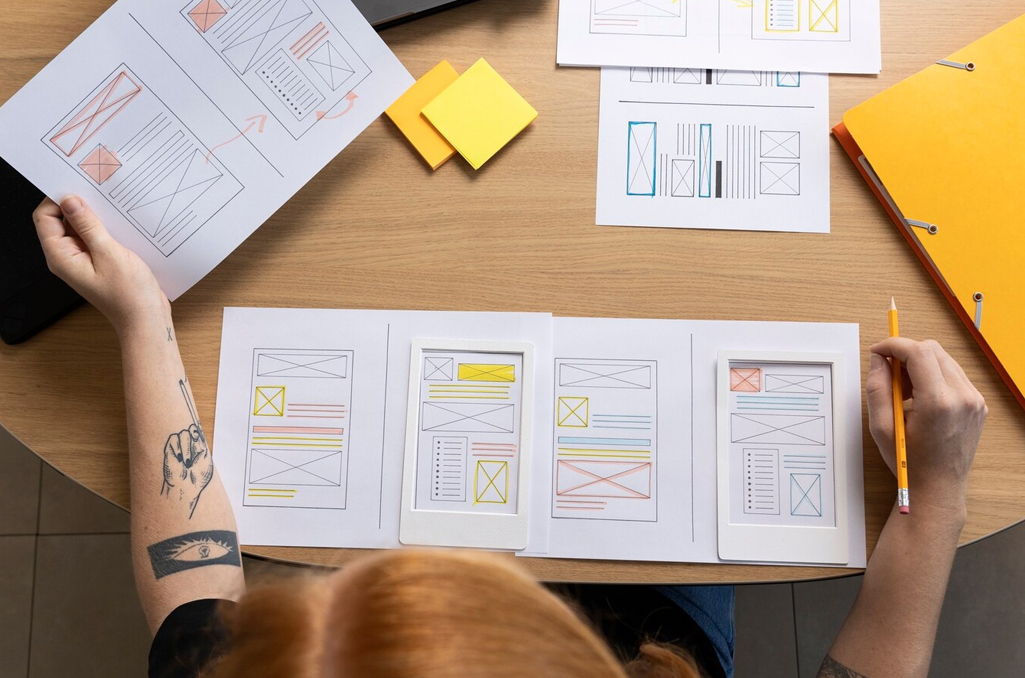
2) Bringing Concepts to Life with Prototyping
- Interactive Prototypes: Prototyping involves creating interactive, high-fidelity mockups of the app. These prototypes simulate the app’s functionality, allowing users to interact with the interface as they would in the actual app. Prototyping tools like InVision or Figma enable the development of clickable prototypes.
- User Testing and Feedback: Prototypes are invaluable for user testing. They allow developers to gather feedback from potential users, evaluate how intuitive the navigation is, and identify pain points. Iterative prototyping, based on user feedback, refines the app’s design, ensuring it meets user expectations.
3) UI/UX Prioritization to Focus on User Experience
- Intuitive Navigation: Users should be able to navigate the app without confusion. Intuitive navigation ensures that users can easily find what they’re looking for. Clear menu structures, intuitive buttons, and logical pathways enhance user experience.
- Responsive Design: With the plethora of devices and screen sizes, responsive design ensures the app adapts seamlessly to different screens. Elements should resize and reorganize intelligently, providing a consistent experience across devices.
- Visually Appealing Interfaces: Aesthetics matter. Visual elements, such as color schemes, typography, and imagery, should be thoughtfully chosen to create an appealing visual experience. Engaging visuals enhances user satisfaction and contributes to the overall user perception of the app.
4) Building Brand Cohesion with Consistent Design Language
- Aligning with Brand Identity: The app’s design elements, including colors, fonts, and imagery, should align harmoniously with the overall brand identity. Consistency in design reinforces brand recognition and creates a cohesive user experience across all touchpoints.
- Creating a Unified Experience: Users should feel a sense of continuity as they transition from the app to other brand platforms. A consistent design language ensures that users can recognize and connect with the brand, fostering trust and loyalty.
Step 3: Development – Coding the Vision
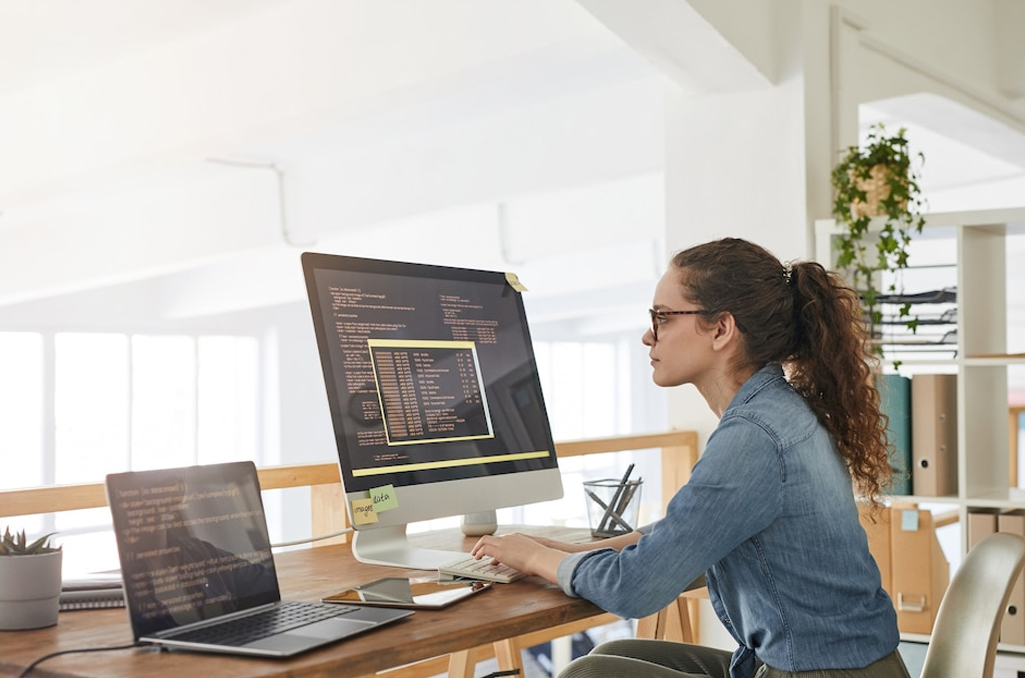

1) Development Approach
- Native Development: Native apps are platform-specific, built for a particular operating system, like iOS or Android. They are optimized for the specific platform, utilizing platform-specific APIs and tools. This approach ensures maximum performance and access to native device features but requires separate development for each platform, often doubling the development effort.
- Hybrid Development: Hybrid apps are built using web technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) and are wrapped in a native container. Tools like React Native and Flutter allow developers to create hybrid apps, providing a balance between platform independence and native-like performance. Hybrid apps can run on both iOS and Android platforms, sharing a significant portion of the codebase.
- Web Development: Web apps are accessed through web browsers on various devices. They are platform-independent and can be built using web technologies. Web apps are versatile and can be accessed from any device with a compatible browser. However, they may have limited access to device-specific features compared to native or hybrid apps.
2) Programming Languages
- Swift (iOS): Swift is Apple’s programming language specifically designed for iOS, macOS, watchOS, and tvOS app development. It is known for its speed and safety features, making it a preferred choice for iOS app developers.
- Kotlin (Android): Kotlin is a modern programming language endorsed by Google for Android app development. It is interoperable with Java, which means developers can use Kotlin alongside existing Java codebases. Kotlin is lauded for its conciseness and enhanced safety features.
- JavaScript (Web): JavaScript is the backbone of web development. It is a versatile scripting language used for creating interactive and dynamic web content. In the context of mobile apps, JavaScript is often used for web-based applications and in conjunction with frameworks like React Native.
3) Frameworks
- React Native: Developed by Facebook, React Native allows developers to build mobile apps using JavaScript and React. It offers a rich set of components and enables the creation of cross-platform apps, sharing a substantial portion of the codebase between iOS and Android.
- Flutter: Created by Google, Flutter is a UI toolkit that enables the development of natively compiled applications for mobile, web, and desktop from a single codebase. Flutter uses the Dart programming language and offers a rich set of pre-designed widgets for building intuitive user interfaces.

Flutter Performance & Code Quality Checklist
Get your free copy
4) Collaborative Development
- Version Control Systems (e.g., Git): Version control systems like Git enable multiple developers to collaborate on a single project simultaneously. Developers can work on different parts of the codebase independently, and changes are merged systematically. Git also tracks changes, allowing for easy rollback if issues arise.
- Agile Methodologies: Agile development is an iterative approach where the project is divided into small increments with minimal planning and changes can be made as the project progresses. Agile methodologies, including Scrum and Kanban, promote collaboration, adaptability, and continuous feedback. They allow development teams to respond promptly to changing requirements and deliver a high-quality product in an agile and efficient manner.
Step 4: Testing – Ensure the Quality and Functionality

1) Functionality Testing
- Verification of Features: Functionality testing involves systematically verifying each feature and functionality of the app to ensure they work as intended. This includes interactive elements, data processing, user inputs, and outputs. Test cases are designed to cover various usage scenarios, ensuring comprehensive coverage of the app’s capabilities.
- Error Handling: Functionality tests assess the app’s ability to handle errors gracefully. This includes scenarios such as network interruptions, incorrect user inputs, or unexpected events. Proper error handling ensures the app doesn’t crash and provides meaningful error messages to users.
2) Performance Testing
- App Speed Optimization: Performance testing evaluates the app’s speed and responsiveness under different conditions, such as varying network speeds and device capabilities. Optimizing app speed ensures swift loading times, smooth transitions, and responsive user interactions, contributing to a positive user experience.
- Resource Usage Optimization: Performance tests assess the app’s resource consumption, including CPU usage, memory utilization, and battery drain. Optimizing resource usage ensures the app operates efficiently without draining the device’s resources excessively, enhancing both performance and user satisfaction.
3) Compatibility Testing
- Diverse Device Testing: Compatibility testing involves running the app on a variety of devices, including smartphones, tablets, and potentially wearables. This ensures the app’s layout and functionality remain consistent across different screen sizes and resolutions.
- Operating System Compatibility: The app is tested on different operating systems (e.g., iOS, Android) and versions to ensure compatibility. Operating system-specific features and behaviors are taken into account to prevent issues that may arise due to OS differences.
- Browser Compatibility (for web apps): In the case of web apps, compatibility testing involves checking the app’s performance and appearance across various web browsers (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, Safari). Ensuring cross-browser compatibility guarantees a consistent experience for web users.
4) Security Testing

Mobile App Security Testing Checklist
Get your free copy
- Vulnerability Identification: Security testing aims to identify potential vulnerabilities within the app, such as data leaks, unauthorized access points, or insecure connections. Techniques like penetration testing are employed to simulate real-world attacks and identify weak points in the app’s security infrastructure.
- Data Encryption: Sensitive user data, both at rest and during transmission, should be encrypted to protect it from unauthorized access. Security tests verify the strength of encryption algorithms and protocols used to safeguard user information.
- User Privacy Protection: Apps often collect user data and protecting user privacy is paramount. Security testing assesses the app’s data handling practices, ensuring compliance with privacy regulations and safeguarding user information from misuse.
Step 5: Deployment – Give The Stage to Your App

The deployment, marketing, and maintenance stage is about ensuring the app not only reaches the users but also continues to meet their needs and expectations.
1) For Deploying to iOS App Store
- Apple Developer Account: To deploy an app on the iOS App Store, developers need an Apple Developer Account, which involves a detailed registration process including verification of identity and payment information.
- App Submission: Apps for iOS are developed using languages like Swift or Objective-C and are submitted to the App Store through Xcode, Apple’s official integrated development environment (IDE). Developers need to create an App ID, provisioning profiles, and certificates to sign and package the app for submission.
- App Review: Apple conducts a rigorous review process to ensure the app complies with its guidelines and standards. It involves checking for UI/UX design consistency, functionality, security measures, and adherence to privacy policies.
- Release: Once the app passes the review, developers set the release date and make the app live on the App Store. Users can find, download, and install the app directly from their iOS devices.
2) For Deploying to Google Play Store
- Google Play Console: Developers need a Google Play Console account to publish Android apps. The console provides tools for managing app releases, tracking app performance, and analyzing user feedback.
- App Submission: Android apps are typically developed using Java or Kotlin. The APK (Android Package) file, which contains the compiled code and resources, is uploaded to the Google Play Console. Developers specify details like app titles, descriptions, screenshots, and other assets.
- Content Rating: Developers complete a content rating questionnaire, classifying the app’s content based on maturity levels. This rating helps users understand the app’s suitability for different age groups.
- App Review: Google Play conducts automated checks for security vulnerabilities and policy violations. If flagged, manual reviews are performed by Google Play staff. Compliance with policies regarding user data, advertisements, and in-app purchases is crucial.
- Release: After approval, developers can publish the app, making it available for download and installation to Android devices globally.
3) App Store Optimization (ASO) Strategies
Keyword Research: Developers use keyword research tools (e.g., Google Keyword Planner) to identify relevant and high-traffic keywords. This research informs the selection of keywords for integration into the app’s metadata.
Metadata Optimization: Keywords are strategically placed in the app title, subtitle, description, and developer name. Careful keyword placement enhances search visibility and increases the likelihood of the app being discovered by users. The app description clearly conveys the app’s features, benefits, and unique selling points. It is concise yet informative, captivating users’ attention and encouraging them to download the app.
For global reach, app descriptions are often localized, ensuring they are culturally relevant and linguistically accurate for different target markets.
App icons and screenshots are meticulously designed to be visually appealing and representative of the app’s features. High-resolution assets ensure clarity on different devices, enhancing the overall user experience.
Developers conduct A/B tests with different visuals to identify which combinations result in higher conversion rates. Data-driven decisions optimize visuals for better user engagement.
How Long It Takes: Mobile App Development Timeframe
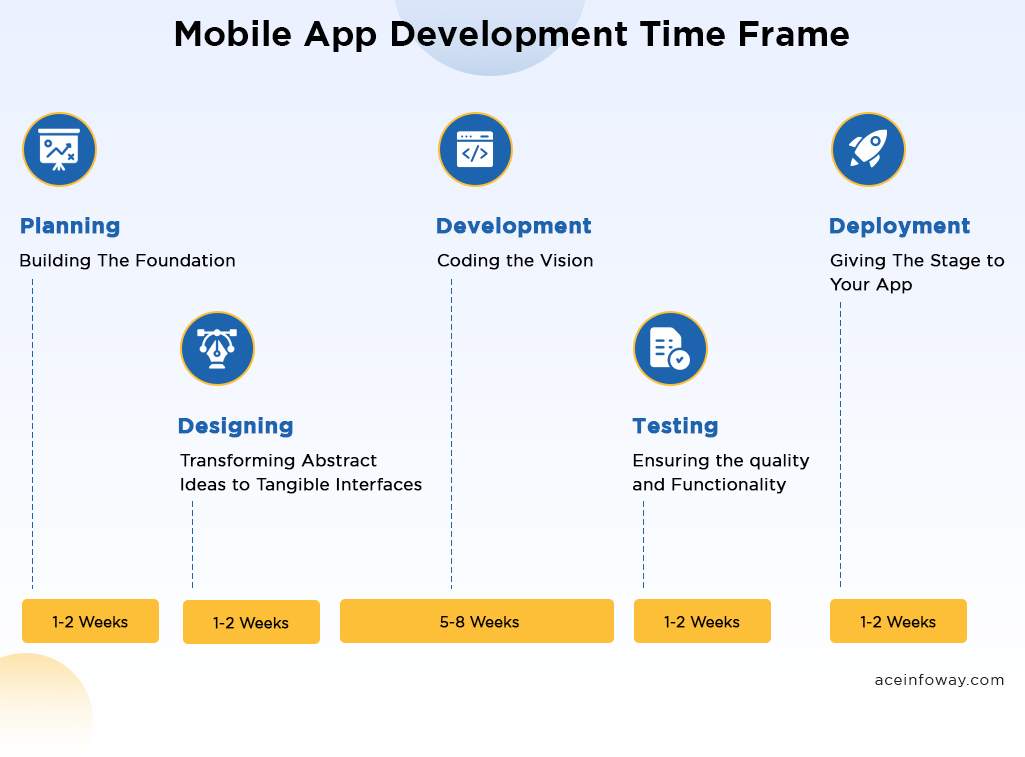
In the intricate world of mobile app development, planning sets the stage, followed by the creative design process. Development breathes life into the concept, testing ensures perfection, and deployment brings the app to the users’ fingertips. Each step is a vital stitch in the vibrant tapestry of app creation, weaving innovation and functionality seamlessly into every pixel and code.
Post-Launch Essentials:
1) Social Media Promotion:
- Engagement: Developers actively engage with the audience through social media platforms. They share updates, respond to user comments, and conduct polls or contests to maintain a strong social media presence.
- Content Strategy: Engaging content, such as videos, blog posts, and infographics, is created and shared across social media channels. Content showcases app features, user testimonials, and industry-related news to capture users’ interest.
2) Influencer Marketing:
- Identifying Influencers: Developers identify influencers whose audience aligns with the app’s target demographic. Influencers are approached for collaborations, including sponsored posts, reviews, or endorsements.
- Authenticity: Authentic partnerships are emphasized, ensuring influencers genuinely appreciate the app and can provide sincere endorsements. Authenticity fosters trust among the influencer’s audience.
3) App Analytics:
- Implementation: Analytics tools (e.g., Google Analytics for Mobile Apps, Flurry Analytics) are integrated into the app. Custom events and user interactions are tracked to gather data on user behavior, retention rates, popular features, and app performance.
- Data Analysis: Developers analyze user data to gain insights into user engagement patterns. This analysis informs decisions regarding feature enhancements, marketing strategies, and user experience improvements.
Steps to Mobile App Maintenance
1) Regular Updates:
- Feature Enhancement: Regular updates introduce new features, enhancements, and optimizations. Developer responses to user feedback and emerging trends inform feature prioritization and implementation.
- Bug Fixes: Bugs reported by users or identified through analytics are addressed promptly. Developers conduct rigorous testing to ensure bug fixes do not introduce new issues.
2) User Feedback Analysis:
- Feedback Channels: Developers collect feedback through app store reviews, in-app feedback forms, and customer support channels. Feedback is categorized, analyzed, and prioritized based on the frequency and severity of issues reported.
- Iterative Improvement: User feedback guides iterative improvements. Developers incorporate user suggestions and address pain points, enhancing the app’s functionality and user experience.
3) Ongoing Maintenance:
- Server Maintenance: For apps with server-side components, regular maintenance of servers ensures optimal performance and minimal downtime. Security patches and updates are applied to protect against vulnerabilities.
- Adaptation to OS Updates: Developers monitor platform updates (iOS, Android) and adapt the app to new APIs and guidelines. Compatibility with the latest OS versions is essential to maintain functionality.
Final Thoughts
Building a successful app can be a challenging endeavor. Whether you’re venturing into app development for the first time or have a history of creating multiple applications, there’s always room for growth and enhancement. Instead of making uninformed decisions about your choice of an app development partner, it’s wise to educate yourself about the process.
At Ace Infoway, we specialize in transforming app ideas into reality. Let our experts guide you through the complexities of app development, ensuring your vision translates into a seamless, user-friendly, and innovative application. Get in touch with us today to embark on your app development journey.
























