Table of Contents
A business intelligence strategy is a systematic approach designed to gather, process, analyze, and utilize data to facilitate informed decision-making aimed at enhancing business growth and operational efficiency. This involves the deployment of various technologies, tools, and methodologies to extract valuable insights from vast amounts of data generated within and outside an organization. Through data collection from diverse sources, thorough analysis using statistical techniques and algorithms, and advanced data visualization and reporting tools, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of their operations, market trends, customer behavior, and other relevant factors.
By integrating these insights into decision-making processes, businesses can identify growth opportunities, optimize operational processes, mitigate risks, and ultimately drive strategic initiatives that align with organizational objectives.
The 5 Key Metrics for Business Intelligence Strategy
Metrics foster accountability and transparency within an organization by establishing clear expectations and objectives. They enable stakeholders to monitor progress towards strategic goals, identify deviations from the desired trajectory, and take corrective actions as necessary to stay on course.
Let us check out the 5 key metrics to help you with efficient growth!
Metric #1 – Revenue Growth
For businesses, revenue growth is paramount as it directly impacts profitability, market share, and overall success. Sustained revenue growth is often a sign of a healthy and thriving business, while stagnant or declining revenue can indicate underlying issues that need to be addressed.
Definition- Revenue growth is a key metric that measures the increase in a company’s total revenue over a specific period. It is a fundamental indicator of a business’s financial health and vitality. Revenue growth reflects the effectiveness of a company’s sales and marketing efforts, as well as its ability to attract and retain customers.
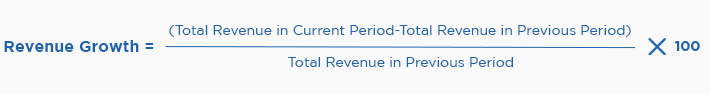
How to Measure Revenue Growth?
Revenue growth is typically calculated by comparing the total revenue generated in a given period (such as a quarter or a year) to the revenue generated in the same period of the previous year. The formula for calculating revenue growth is:
Importance of Tracking Revenue Trends
Tracking revenue trends is essential for businesses to assess their financial performance and make informed decisions. By monitoring revenue growth over time, companies can identify patterns, pinpoint areas of strength and weakness, and adjust their strategies accordingly.
For instance, if revenue growth is consistently positive, it may indicate that current business strategies are effective and should be continued or expanded. Conversely, if revenue growth is declining or fluctuating, it may signal the need for strategic changes, such as investing in new marketing initiatives, improving product offerings, or entering new markets.
Metric #2 – Customer Acquisition Cost
The importance of CAC lies in its ability to provide insights into the profitability and sustainability of customer acquisition efforts. By comparing CAC to the lifetime value of a customer (LTV), businesses can determine whether their acquisition costs are justified by the revenue generated from acquired customers. Maintaining a healthy CAC-to-LTV ratio is crucial for ensuring long-term profitability and business growth.
Definition- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is a metric that measures the cost a company incurs to acquire a new customer. It encompasses all expenses related to marketing, sales, and promotional activities aimed at attracting and converting prospects into paying customers. Understanding and managing CAC is essential for businesses to assess the effectiveness and efficiency of their customer acquisition strategies.
How to Calculate CAC?
Calculating CAC involves summing up all expenses related to acquiring customers within a specific period and dividing that total by the number of customers acquired during the same period. The formula for calculating CAC is:
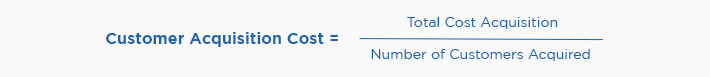
Total Cost of Acquisition includes expenses such as marketing campaign costs, sales team salaries, advertising expenditures, and any other costs directly attributable to customer acquisition efforts.
Significance of CAC in Business Intelligence
CAC serves as a critical metric in business intelligence as it provides valuable insights into the effectiveness and efficiency of customer acquisition strategies. By analyzing CAC trends over time, businesses can identify areas for optimization and improvement in their marketing and sales processes.
Additionally, CAC can help businesses allocate their marketing budgets more efficiently by identifying which acquisition channels yield the highest return on investment (ROI). For example, if the CAC for leads generated through social media advertising is significantly lower than the CAC for leads obtained through traditional print advertising, businesses may choose to reallocate resources towards social media advertising to maximize their ROI.
Furthermore, tracking CAC allows businesses to forecast future customer acquisition costs accurately and plan their budgets accordingly. By incorporating CAC data into their business intelligence analyses, companies can make data-driven decisions that drive sustainable growth and profitability over time.
Metric #3 – Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Understanding CLV is crucial for businesses as it provides insights into the profitability of customer relationships and helps prioritize resources toward high-value customers. By focusing on maximizing CLV, businesses can optimize their marketing, sales, and customer service strategies to enhance customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention.
Definition- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is a metric that represents the total revenue a business can expect to generate from a single customer throughout their entire relationship with the company. It takes into account factors such as purchase frequency, average order value, and customer retention rate to estimate the long-term value of each customer to the business.
How to Calculate CLV?
Calculating CLV involves analyzing historical customer data to determine the average revenue generated from each customer over their entire relationship with the company. There are several methods for calculating CLV, including:
- Historic CLV: This method calculates CLV based on past customer behavior and revenue data.
- Predictive CLV: This method uses predictive analytics techniques to forecast future customer behavior and estimate CLV.
- Cohort Analysis: This method groups customers based on similar characteristics or behaviors and analyzes their lifetime value within each cohort.
The formula for calculating CLV may vary depending on the method used, but it typically involves factors such as average purchase value, purchase frequency, customer lifespan, and retention rate.
Why CLV is Essential for Business Intelligence Strategy?
CLV plays a crucial role in shaping a business intelligence strategy by providing valuable insights into customer profitability and long-term revenue potential. Here’s why CLV is essential for business intelligence strategy:
- Strategic Decision Making: CLV helps businesses prioritize resources and investments towards acquiring and retaining high-value customers. By focusing on customers with the highest CLV, businesses can maximize their return on investment and drive sustainable growth.
- Customer Segmentation: CLV enables businesses to segment their customer base into different categories based on their value to the company. This allows businesses to tailor their marketing, sales, and service strategies to meet the specific needs and preferences of each customer segment.
- Customer Retention: CLV highlights the importance of customer retention in driving long-term profitability. By understanding the factors that influence CLV, businesses can implement strategies to improve customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention, ultimately increasing CLV and maximizing lifetime customer value.
Metric #4 – Churn Rate
Churn rate helps identify areas of weakness in your business products, services, or customer experience that may be driving customers away. By monitoring churn rate, businesses can take proactive measures to improve customer satisfaction, address issues, and retain customers, ultimately driving long-term profitability and sustainability.
Definition- Also known as customer attrition rate, Churn Rate is a metric that measures the percentage of customers who stop using a company’s products or services over a specific period. It is a crucial indicator of customer retention and loyalty and is closely tied to a company’s revenue and growth prospects.
How to Calculate Churn Rate?
Calculating the churn rate involves dividing the number of customers who churned during a given period by the total number of customers at the beginning of that period, then multiplying the result by 100 to express it as a percentage. The formula for calculating the churn rate is:

Impact of Churn Rate on Business Intelligence
Churn rate has a significant impact on business intelligence as it provides valuable insights into customer behavior and satisfaction. Here’s how churn rate influences business intelligence:
- Predictive Analytics: Churn rate data can be used to develop predictive models that forecast future churn and identify at-risk customers. By analyzing historical churn patterns and customer characteristics, businesses can proactively intervene to prevent churn and retain valuable customers.
- Customer Segmentation: Churn rate data enables businesses to segment their customer base into different categories based on their likelihood of churning. This allows businesses to tailor their marketing, sales, and retention strategies to meet the specific needs and preferences of each customer segment, improving overall customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Product and Service Improvement: High churn rates may indicate underlying issues with product quality, customer service, or pricing that need to be addressed. By analyzing churn rate data alongside other customer feedback and satisfaction metrics, businesses can identify areas for improvement and implement targeted strategies to enhance the customer experience and reduce churn.
Metric #5 – Return on Investment (ROI)
Knowing about ROI helps you make informed decisions about resource allocation, prioritizing investments, and optimizing business performance. By calculating ROI, businesses can identify which initiatives yield the highest returns and focus their efforts on activities that drive the greatest value and impact.
Definition- Return on Investment (ROI) is a financial metric that measures the profitability or efficiency of an investment relative to its cost. It is a key indicator of the success and effectiveness of business initiatives, projects, or campaigns. ROI is essential for businesses as it helps assess the value generated from investments and allocate resources more efficiently.
How to Calculate ROI?
ROI is typically calculated by dividing the net profit generated from an investment by the total cost of the investment, then multiplying the result by 100 to express it as a percentage. The formula for calculating ROI is:

Net profit is calculated by subtracting the total cost of the investment from the total revenue or benefits generated from the investment.
Role of ROI in Evaluating Business Intelligence Initiatives
ROI plays a critical role in evaluating the effectiveness of business intelligence initiatives and data-driven projects. Here’s how ROI contributes to business intelligence strategy:
- Performance Measurement: ROI provides a quantitative measure of the value generated from business intelligence initiatives, such as implementing new analytics tools, data infrastructure improvements, or data-driven decision-making processes. By comparing the ROI of different initiatives, businesses can assess their impact on profitability and prioritize investments accordingly.
- Resource Allocation: ROI helps businesses allocate resources more effectively by identifying which business intelligence initiatives deliver the highest returns. By focusing resources on initiatives with the highest ROI, businesses can maximize their overall return on investment and drive sustainable growth.
- Continuous Improvement: Monitoring ROI enables businesses to track the performance of their business intelligence initiatives over time and identify opportunities for optimization and improvement. By analyzing ROI trends and adjusting strategies as needed, businesses can ensure that their business intelligence efforts remain aligned with organizational goals and objectives.
 Many of the tools offer free trials or demo versions, allowing businesses to test them out before committing to a purchase. These tools are designed to help businesses collect, track, and analyze data more effectively, enabling them to gain deeper insights into their performance and make more informed decisions. Here are some examples of tools that may be useful for measuring the key metrics discussed:
Many of the tools offer free trials or demo versions, allowing businesses to test them out before committing to a purchase. These tools are designed to help businesses collect, track, and analyze data more effectively, enabling them to gain deeper insights into their performance and make more informed decisions. Here are some examples of tools that may be useful for measuring the key metrics discussed:
Major Takeaways for Your Business
- Continuously monitor and analyze.
- Focus on actionable insights.
- Integrate data sources.
- Invest in analytics tools and technology.
- Embrace a data-driven culture.
- Stay agile and adaptive.
- Seek continuous improvement.
Harnessing the power of business intelligence strategy can revolutionize your company’s operations and drive sustainable growth. Ready to unlock your business’s full potential? Contact us today to learn how our tailored BI solutions can elevate your performance and propel you toward success.

Reasons Why Software Projects Burn Cash [Whitepaper]
Get your free copy