Table of Contents
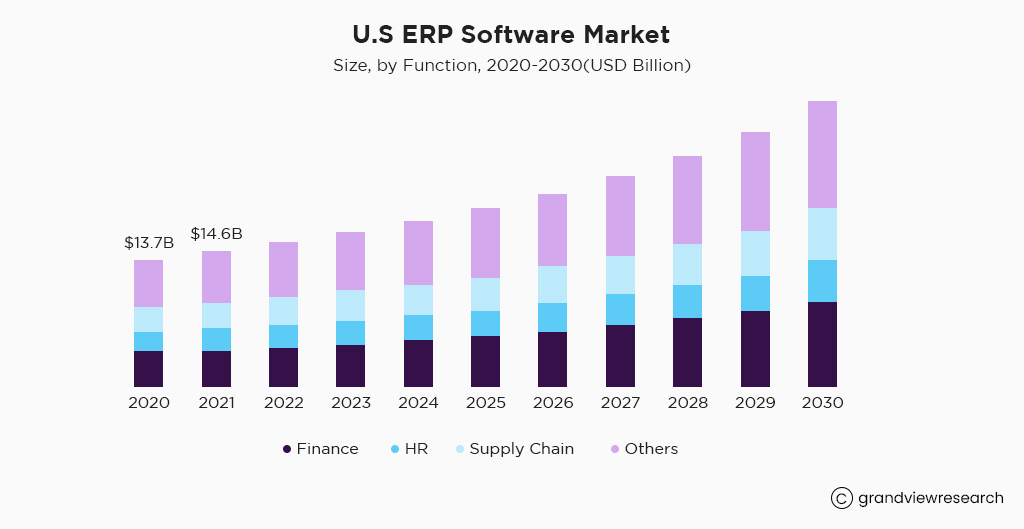
The prominence of ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software extends far beyond its impressive market valuation in 2022. As we reflect on the monumental USD 54.76 billion figure, it becomes evident that ERP software is not just a solution; it’s a transformative force that shapes the trajectory of modern businesses.
The fact that the global ERP software market has set the stage for a substantial 11.0% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) from 2023 to 2030 is a testament to the enduring relevance and impact of this technology. This isn’t just a mere statistical projection; it’s a revelation of how ERP software will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping business strategies, operational efficiency, and sustained growth.
The dynamic nature of ERP software’s evolution holds a narrative that resonates across industries, from manufacturing to services, finance to healthcare, and beyond. Its significance lies in its ability to seamlessly integrate diverse business functions, providing a holistic view of operations, optimizing resource allocation, and facilitating data-driven decision-making.
Let’s dissect this insight and make it evident that ERP software isn’t just a trend!
What is ERP Software for Businesses?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software for businesses is an integrated suite of software applications designed to facilitate efficient and streamlined management of various business processes and functions within an organization. It serves as a centralized platform that enables real-time data sharing, automation, and collaboration across departments, helping enterprises enhance operational efficiency, make informed decisions, and achieve their strategic goals.
Key Modules of ERP Software in Businesses
ERP software encompasses a variety of modules that address different aspects of business operations. Here are some key modules commonly found in ERP software for businesses:
- Finance and Accounting: This module manages financial transactions, including accounts payable, accounts receivable, general ledger, budgeting, and financial reporting. It provides a comprehensive view of an organization’s financial health.
- Human Resources (HR): The HR module covers employee information, payroll processing, benefits administration, time and attendance tracking, recruitment, performance management, and training.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): SCM modules oversee procurement, inventory management, order fulfillment, demand forecasting, supplier management, and logistics, ensuring an efficient flow of materials and goods.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturing modules handle production planning, scheduling, work order management, shop floor control, quality control, and maintenance, optimizing the manufacturing process.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): CRM modules manage customer interactions, sales leads, opportunities, marketing campaigns, and customer support, fostering stronger customer relationships.
- Sales and Distribution: This module tracks sales orders, manages pricing, handles order fulfillment, monitors shipping and distribution, and maintains customer records.
- Project Management: The project management module assists in planning, executing, and monitoring projects, allocating resources, tracking progress, and managing project budgets.

Software Development: Best Practices of Build Your Own Team (BYOT)
Get your free copy
- Inventory Management: This module tracks inventory levels, monitors stock movements, manages reorder points, and ensures efficient inventory control.
- Procurement: Procurement modules handle vendor management, purchase orders, requisitions, and supplier performance evaluations, optimizing the procurement process.
- Quality Management: Quality management modules focus on maintaining and improving product and service quality by implementing quality control processes, managing audits, and tracking non-conformances.
- Warehouse Management: This module optimizes warehouse operations by managing storage locations, organizing picking and packing processes, and improving inventory accuracy.
- Business Intelligence (BI) and Analytics: BI modules provide tools for generating reports, dashboards, and analytics to derive insights from the data stored in the ERP system.
- Risk Management and Compliance: This module assists in identifying and managing risks, ensuring compliance with industry regulations and standards, and maintaining data security.
- Service Management: Service management modules handle after-sales service processes, including service requests, warranty management, field service scheduling, and customer support.
Often customizable and adaptable to an organization’s needs, collectively form an integrated ERP system that streamlines various business functions and promotes efficient collaboration across departments. The choice of modules depends on the specific requirements and industry of the business.
How ERP Software Improves Productivity in Business Processes?
ERP software emerges as a technological powerhouse that revolutionizes productivity across an array of critical business processes. This multifaceted solution operates a unique blend of technical prowess and strategic expertise, seamlessly weaving its capabilities into the very fabric of operations.
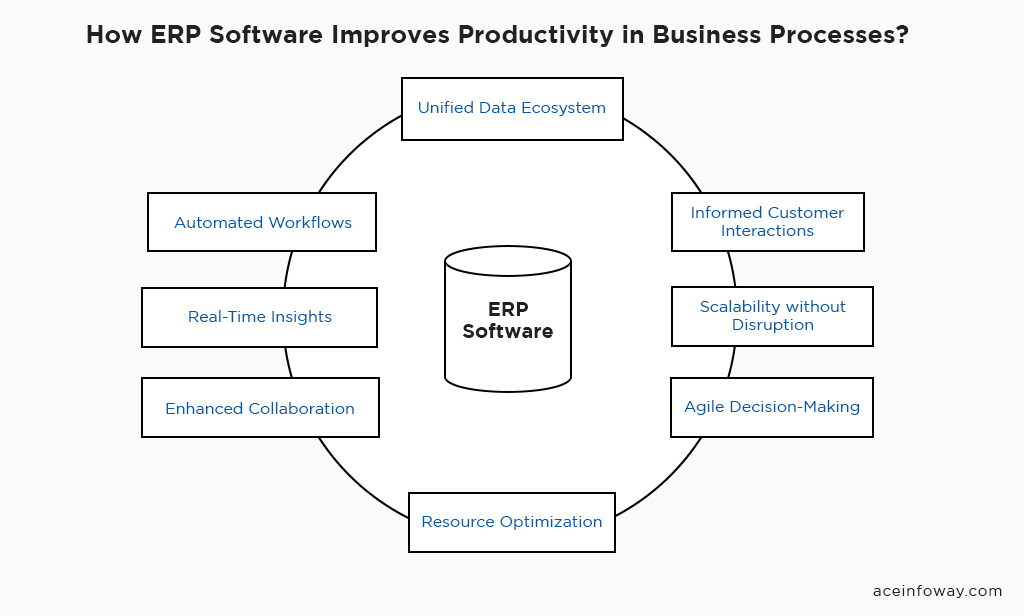
- Unified Data Ecosystem: Imagine the efficiency of having a single source of truth. ERP software establishes a centralized repository where data from different corners of your organization converges. This empowers decision-makers with accurate and up-to-date information, reducing data silos and enabling them to act swiftly and confidently.
- Automated Workflows: The magic lies in automation. ERP software takes the reins on repetitive and time-consuming tasks, liberating your workforce to focus on strategic endeavors. From invoice processing to inventory management, automation minimizes errors, reduces processing times, and elevates the overall operational tempo.
- Real-Time Insights: The pulse of modern business is real-time. ERP software isn’t just a data repository; it’s a gateway to actionable insights. Dashboards, reports, and analytics unveil trends, patterns, and potential bottlenecks, empowering decision-makers to respond proactively and capitalize on opportunities as they arise.
- Enhanced Collaboration: The synergy within your organization receives a turbocharge. ERP software fosters cross-functional collaboration by bridging communication gaps. Departments share real-time information, aligning goals, and fostering a cohesive environment that fuels productivity.
- Resource Optimization: Efficiency and resource allocation go hand in hand. ERP software optimizes resource utilization by aligning them with demand and capacity. The result? Reduced wastage, smarter allocation, and a streamlined path to achieving operational goals.
- Agile Decision-Making: Today’s business landscape demands agility. ERP software equips decision-makers with the tools to swiftly adapt strategies based on changing market dynamics. With a clear view of operations, they can pivot confidently, gaining a competitive edge.
- Scalability without Disruption: Growth should be exciting, not daunting. ERP software accommodates expansion seamlessly. As you scale, your software scales with you, adapting to new processes and volumes without disrupting the momentum you’ve built.
- Informed Customer Interactions: Your customers deserve the best. ERP software enhances customer experiences by ensuring accurate order processing, timely deliveries, and efficient support. The result? Satisfied customers and enduring relationships.
Key Considerations when Selecting and Customizing ERP Solutions
As you embark on this journey, it’s essential to navigate the complexities with a strategic approach. Following are the technical intricacies of key considerations when choosing and customizing ERP solutions for your business.
Business Requirements Assessment:
- Before diving into ERP selection, conduct a comprehensive assessment of your business requirements. Understand your operational workflows, pain points, and growth goals.
- Engage cross-functional teams to document and prioritize requirements. Analyze your existing systems, identify gaps, and align your needs with the functionalities offered by ERP vendors.
Scalability and Future-Proofing:
- An ERP solution should grow with your business. Scalability is crucial to accommodate increased data, users, and operations as your business expands.
- Evaluate the scalability of ERP systems by examining their architecture and performance capabilities. Opt for solutions that can seamlessly handle increased workloads without compromising performance.
Customization Flexibility:
- ERP customization tailors the system to match your specific needs. Balancing customization with out-of-the-box features is critical to avoid complexity and long-term maintenance challenges.
- Prioritize customization needs based on business-critical requirements. Evaluate ERP solutions that offer a range of customization options while ensuring that essential functionalities are readily available.
Integration Capabilities:
- ERP doesn’t work in isolation; it needs to integrate with existing applications and systems. Seamless integration enhances data accuracy and streamlines processes.
- Examine the ERP’s integration capabilities, including APIs and connectors. Ensure compatibility with your current technology stack and assess the ease of integrating third-party applications.
User Interface and Experience:
- User adoption is key to ERP success. A user-friendly interface and intuitive experience are crucial for smooth onboarding and day-to-day usage.
- Conduct user interface evaluations with potential end-users. Choose ERP solutions that offer a clean and intuitive interface, reducing the learning curve and fostering user engagement.
Data Security and Compliance:
- Protecting sensitive data is paramount. ERP solutions should comply with industry standards and regulations while offering robust security measures.
- Assess the ERP vendor’s security protocols, encryption methods, and compliance certifications. Ensure the solution aligns with your industry’s data security and privacy requirements.
Vendor Reputation and Support:
- Your ERP vendor is a long-term partner. Their reputation, track record, and post-implementation support are vital for a successful ERP journey.
- Research vendors thoroughly, review customer testimonials, and assess their expertise in your industry. Engage in conversations about post-implementation support, updates, and ongoing maintenance.
Training and Change Management:
- ERP adoption involves a learning curve for your workforce. Adequate training and change management strategies are essential for a smooth transition.
- Develop comprehensive training plans that cover different user roles and functionalities. Introduce change management strategies to address resistance and ensure user buy-in.
ERP Software – Future Trends and Innovations
As we step forward, let’s explore the exciting trends that are reshaping ERP, elevating its capabilities, and propelling businesses into a new era of operational excellence.
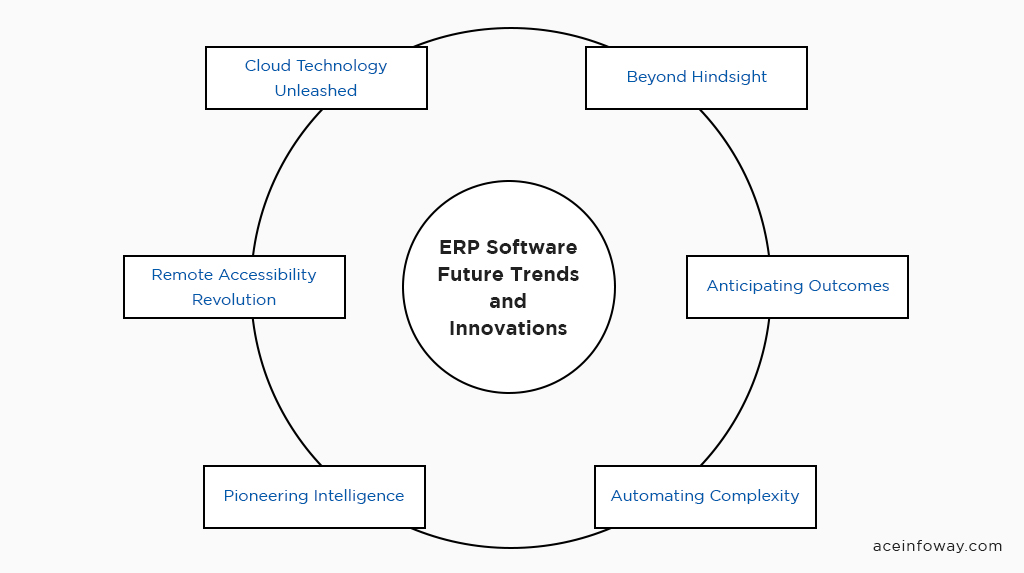
- Cloud Technology Unleashed:
Cloud-based ERP systems are poised to redefine the way businesses manage their operations. Cloud deployment offers a myriad of advantages, from reduced infrastructure costs to heightened flexibility. Organizations can bid farewell to on-premises limitations and embrace a virtual infrastructure that adapts to their growth.
- Remote Accessibility Revolution:
The traditional boundaries of office spaces are dissolving. With cloud-based ERP, remote teams can access critical data and processes from anywhere, ensuring seamless collaboration and uninterrupted operations. This trend amplifies agility and enables organizations to thrive in an era of hybrid work environments.
- Pioneering Intelligence:
The integration of AI and machine learning injects ERP systems with predictive and prescriptive capabilities. These technologies analyze historical data, discern patterns, and offer insights that empower decision-makers to anticipate future trends and make informed choices.
- Automating Complexity:
AI-driven ERP augments automation by handling intricate tasks that once demanded human intervention. From inventory optimization to demand to forecast, AI-driven ERP streamlines processes, minimizes errors, and frees up human resources for strategic endeavors.
- Anticipating Outcomes:
Predictive analytics empowers businesses to foresee outcomes based on historical data and trends. This empowers leaders to proactively address challenges, seize opportunities, and make decisions rooted in foresight.
- Beyond Hindsight:
Gone are the days of relying solely on hindsight. Predictive analytics transforms data into a roadmap for the future, guiding strategic moves with precision. Organizations gain a competitive edge by steering their ship with predictive insights.
As businesses embrace these trends, they carve a path towards resilient, adaptable, and data-driven operations, positioning themselves at the forefront of progress. The future of ERP isn’t just about solutions; it’s about shaping the destiny of businesses in a dynamic digital age.

Guide To Software Product Development By Experts [eBook]
Get your free copy
Wrap-Up
ERP solutions are not just software; they are catalysts for growth, driving your organization toward operational excellence. Embrace a streamlined future where manual tasks are automated, data is at your fingertips, and collaboration transcends boundaries.
Ace Infoway has a team of experts that specializes in creating tailored ERP software aligning with your goals and processes. With our guidance, you can harness the full potential of ERP technology to optimize processes, empower your teams, and make data-driven decisions that define success in the digital age. We are here for you!
Don’t wait—seize the opportunity to optimize processes, empower your teams, and make data-driven decisions that define success in the digital age. Elevate your operations with ERP solutions and pave the way for a future that’s both efficient and productive.